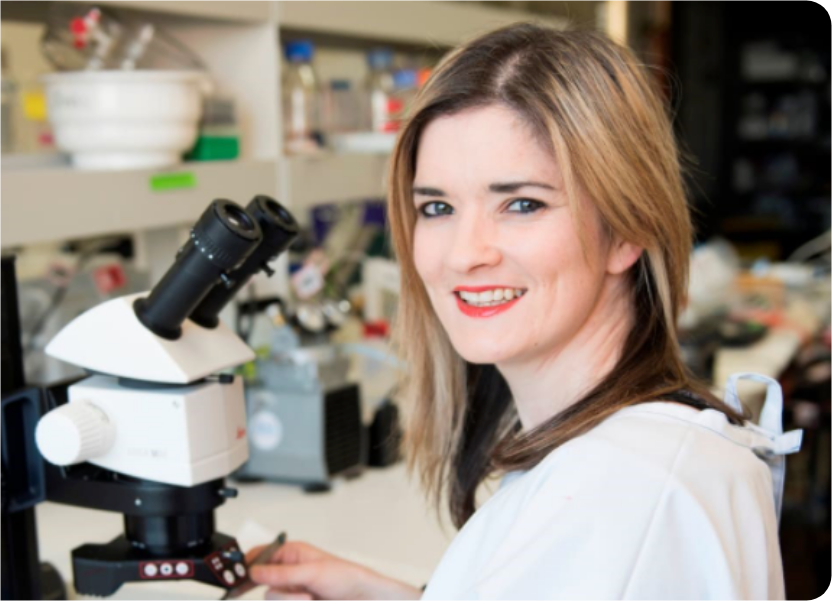
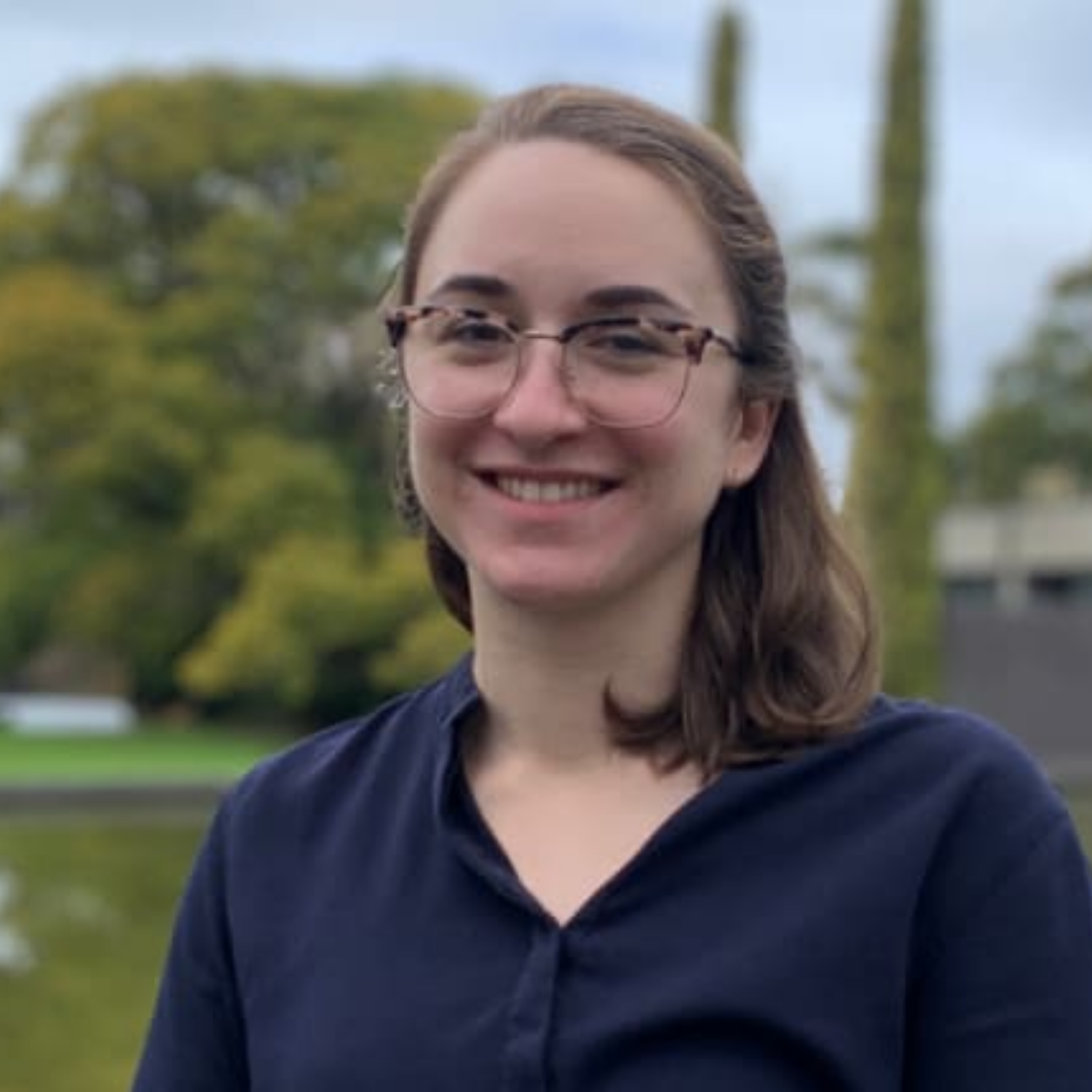
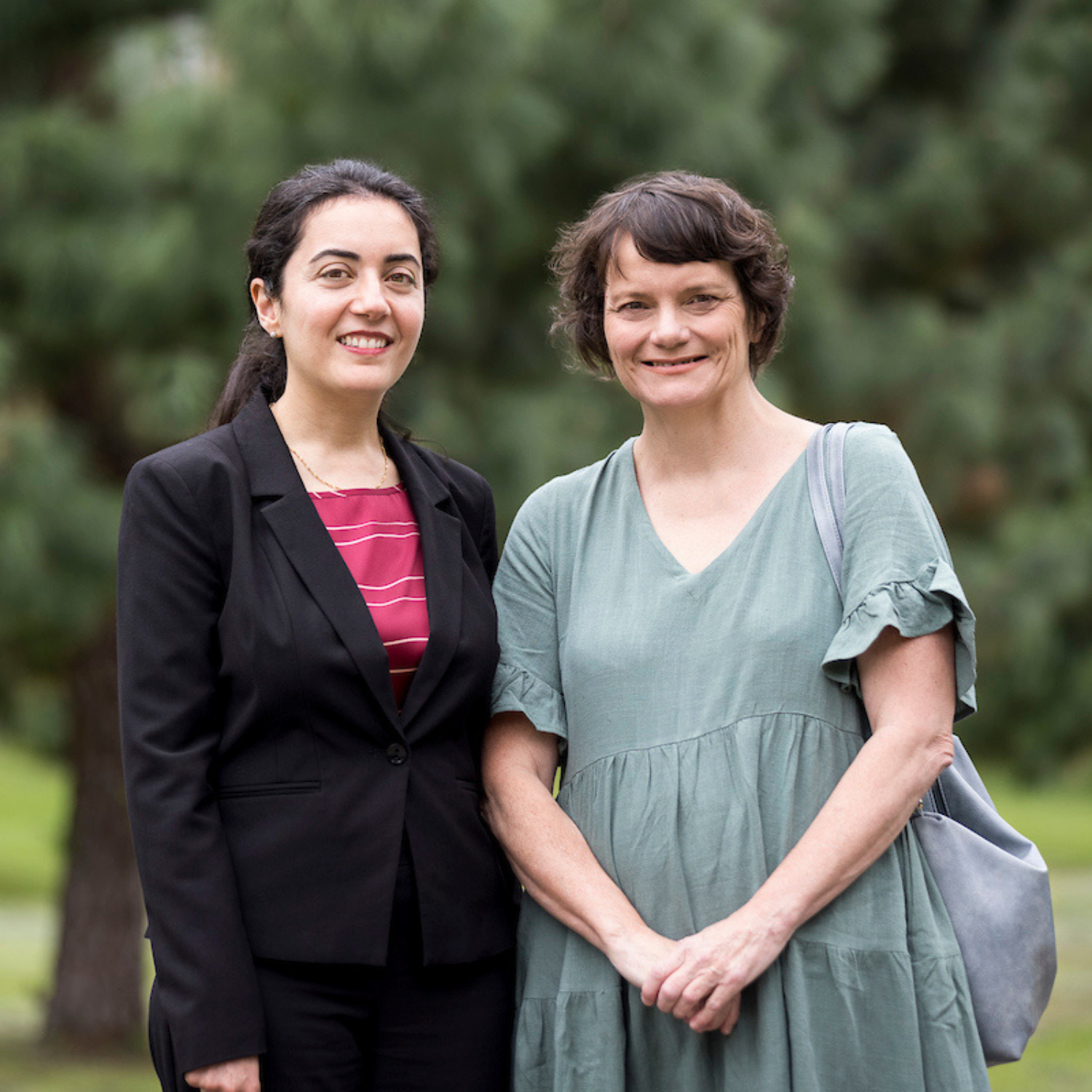
Associate Professor Sophie Payne, Senior Research Fellow, Head of Peripheral Interface Neuromodulation Research Program
Sophie is a Research Fellow at the Bionics Institute (2015–present), Head of the Peripheral Interface Neuromodulation Team and has an honorary position at the University of Melbourne.
She completed her PhD in neuroscience at the University of Western Australia (2010-2013) where she then moved to the University of Melbourne (2013-2015) as a Research Fellow.
Using electricity to alter the activity of nerves, dubbed ‘electroceutical therapy’, has demonstrated success in the treatment of many human diseases.
Her research vision is to progress a pipeline of electroceutical technology towards the clinic to provide clinical relief in a number of diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis and urinary incontinence.
Specifically, Sophie’s specialty is in the use of medical devices in the autonomic nervous system to treat disease.
She conducted preclinical safety and efficacy studies that led to the translation of new technology that electrically stimulates the vagus nerve for the treatment of Crohn’s Disease.
Recently, Sophie’s interests have expanded this research and is investigating vagus nerve stimulation as a therapy of rheumatoid arthritis.
She also has an interest in developing adaptive, closed-loop technology for the treatment of urinary incontinence.
This involves developing novel signal processing technology that decodes neural signals to predict and diagnose disease flare-ups, as well as a stimulation protocol to delay urination.
Sophie’s work in the field of ‘electric medicine’ has led to the publication of 3 patents and nearly 20 papers, some of which supported the successful granting of human ethics approval for an Australia first clinical-trial for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.
Her work has also received media attention including featuring on Channel 7, 9, 10 tonight, ABC 24 evening news and Sunrise morning show, as well as several radio talks (ABC radio with Virginia Trioloi, 3AW, ABC Adelaide, Einstein-a-Go-Go radio) and Herald Sun articles (Brigid O’Connell).
Sophie has been an invited ‘exhibit scientist’ for the Melbourne Museum’s exhibition ‘A Gut Feeling’ during Science Week (2019) and as a presenter at the Museum’s Top Design Education Forum (2023).
Sophie has supervised 14 postgraduate students (Biomedical Research Victoria’s program), is a mentor for PhD and early career researchers (IMNIS) and is actively involved in the ‘Mentoring the Next Generation of Women in STEMM’ program (Bionics Institute and Ivanhoe Girls Grammar School: 2019, 2021).
E: SPayne@bionicsinstitute.org
URL: https://www.bionicsinstitute.org/dr-sophie-payne
ORCID: 0000-0002-3428-2275
Google Scholar: Sophie Payne
Research projects
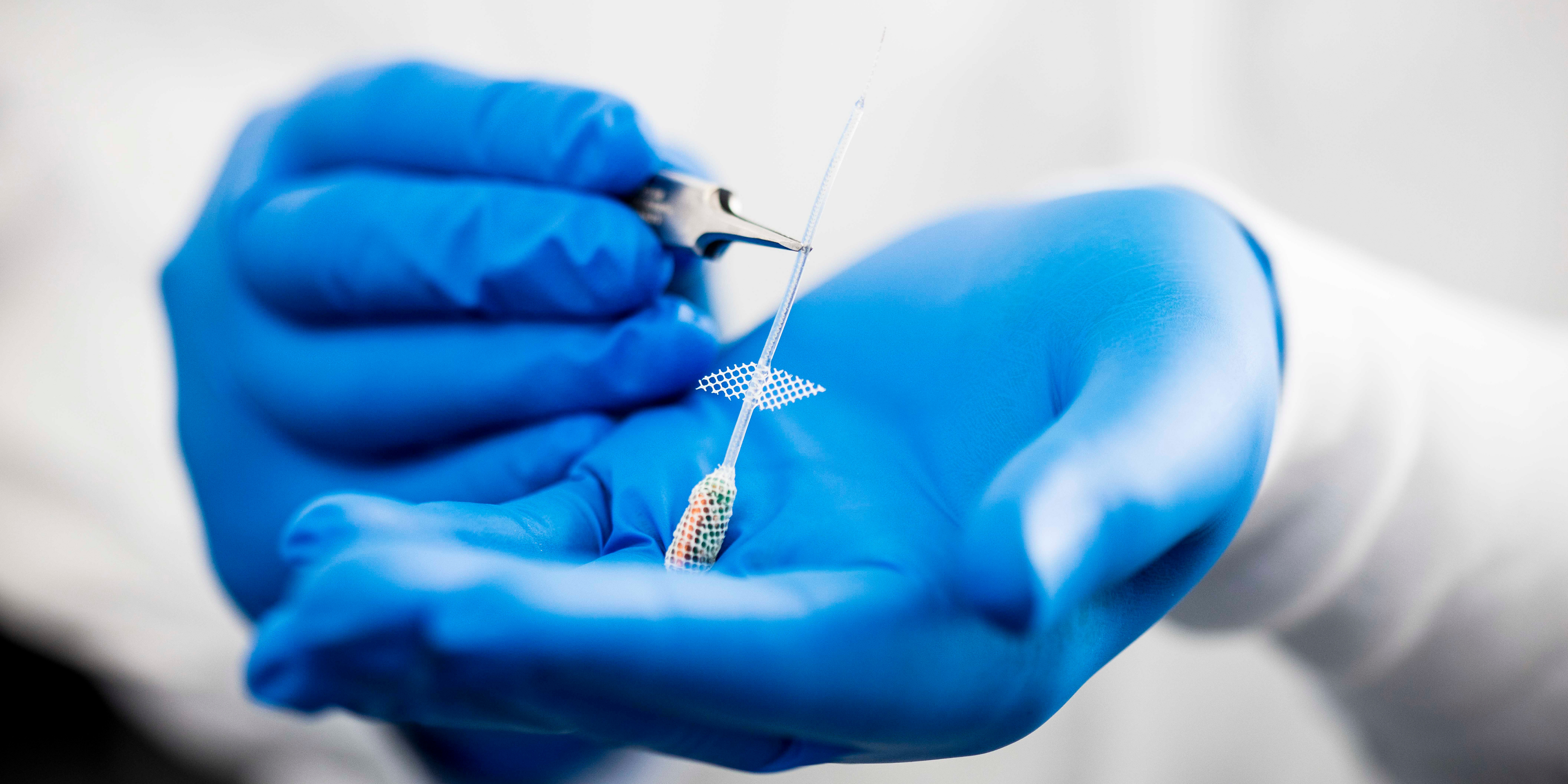
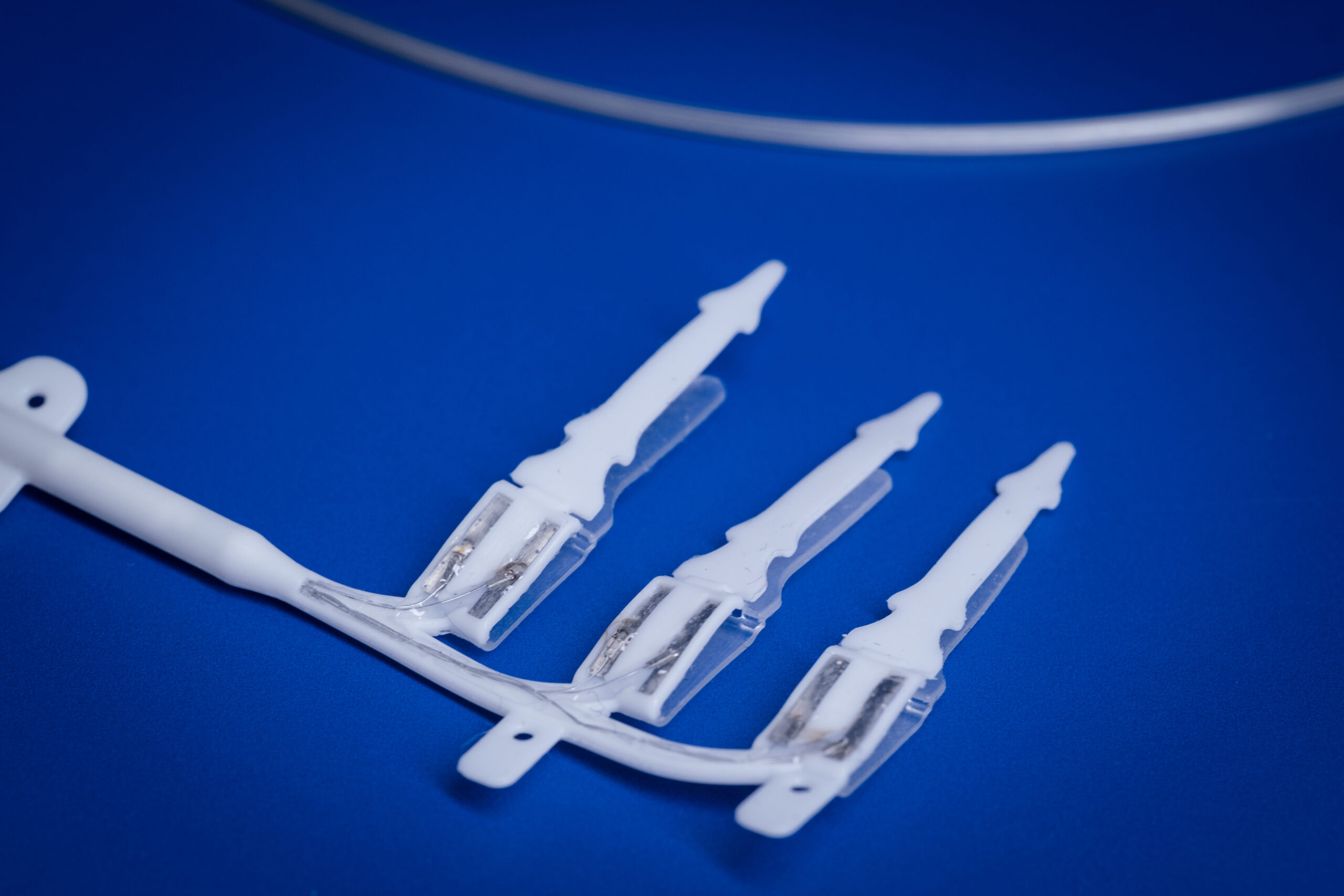
Miniaturised peripheral nerve device development
Closed-loop control of inflammatory bowel disease
Recent publications
1. Payne S.C, Wiedmann N.M, Eiber C.D, Wong A.W, Senn P, Osborne P.B, Keast J.R and Fallon J.B. 2020. Recording of electrically evoked neural activity and bladder pressure responses in awake rats chronically implanted with a pelvic nerve array. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 14:619275. doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.619275
2. Payne S.C, Ward G, MacIsaac R.J, Hyakumura T, Fallon J.B, Villalobos J. 2020. Differential effects of vagus nerve stimulation strategies on glycemia and pancreatic secretions. Physiological reports. 8(11): e14479. doi.org/0.14814/phy2.14479. Full Text
3. Payne, S. C., J. B. Furness, O. Burns, A. Sedo, T. Hyakumura, R. K. Shepherd, and J. B. Fallon. 2019. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Abdominal Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Experimental Intestinal Inflammation. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 13(418). doi.org/3389/fnins.2019.00418. Full Text
4. Payne, S. C., O. Burns, M. J. Stebbing, R. Thomas, A. C. de Silva, A. Sedo, F. Wiessenborn, T. Hyakumura, M. Huynh, C. N. May, R. A. Williams, J. Furness, J. Fallon, and R. Shepherd. 2019. Vagus nerve stimulation to treat inflammatory bowel disease: a chronic, preclinical safety study in sheep. Bioelectronics in Medicine. 1(4): 235-250. doi.org/10.2217/bem-2018-0011.
5. Payne, S. C., J. B. Furness, and M. J. Stebbing. 2018. Bioelectric neuromodulation for gastrointestinal disorders: effectiveness and mechanisms. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology. 16(2): 89-105. doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0078-6 . Full Text